Learn More
Invitrogen™ beta Amyloid Biosimilar Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
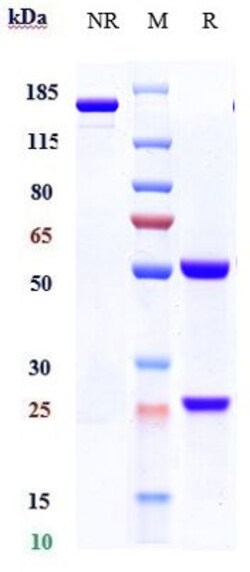
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Marke: Invitrogen™ MA559754
Description
For reconstitution, add sterile, distilled water to achieve a final antibody concentration of 1 mg/mL. Gently shake to solubilize the protein completely. Do not vortex. Reconstituted products should be stored at -80 °. This antibody can also be cross referenced by the term Rockefeller U. patent anti-Amyloid Beta.
Amyloid beta peptide (Abeta/Beta-amyloid) is the major constituent of amyloid plaques in the brains of individuals afflicted with Alzheimer's disease. Abeta peptide is 40-43 amino acids long and generated from the beta-amyloid precursor protein (beta APP) in a two-step process. The first step involves cleavage of the extracellular, amino-terminal domain of beta APP. Protein cleavage is performed by an aspartyl protease, beta-secretase (BACE) which is synthesized as a propeptide and must be modified to the mature and active form by the prohormone convertase, furin. Beta APP cleavage by the mature form of BACE results in the cellular secretion of a segment of beta APP, and a membrane-bound remnant. The remnant protein is processed by another protease, gamma-secretase. Gamma-secretase cleaves an intra-membrane site in the carboxyl-terminal domain of beta APP, thus generating the amyloid beta peptide. Gamma-secretase is believed to be a multi-subunit complex containing presenilin-1 and 2 as central components. The transmembrane glycoprotein, nicastrin, is associated with presinilins and has been found to bind to the carboxyl-terminus of beta APP and helps to modulate the production of the amyloid beta peptide. Abeta is an extracellular filamentous protein component of amyloid cores, neuritic plaques and is also found as a deposit in neurofibrillary tangles. Alzheimer's disease, the most common cause of senile dementia, is characterized by abnormal filamentous protein deposits in the brain. Beta amyloid deposits are also detected in Lewy body dementia, Down's syndrome, amyloidosis (Dutch type), cerebroarterial amyloidosis (cerebral amyloid angiopathy) and in the Guam Parkinson-Dementia complex.
Specifications
| beta Amyloid Biosimilar | |
| Recombinant Monoclonal | |
| Unconjugated | |
| Human | |
| 1 mg | |
| Primary | |
| -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles | |
| Lyophilized |
| ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Functional Assay, Surface Plasmon Resonance | |
| 1 mg/mL | |
| 25 mM histidine with 8% sucrose, 0.01% Tween 80 and no preservative; pH 6.2 | |
| Protein A | |
| RUO | |
| Human | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG1 |
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.